Importance of Last-Mile Connectivity and Global Adoption of Mobile Phones: Trend, Interfering Factors

The economic, social, and political life in the twenty-first century is increasingly becoming digital.

Several factors significantly affect the design and implementation of last-mile telecommunication.

Network solutions and business models need to be autonomous for long-term sustenance.
Increasing economic and educational exposure, and promoting global health and wellness, can be achieved through the power of sharing knowledge, technology, and resources. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) can play a key role in disseminating such knowledge across the world. But a digital divide exists between urban and rural/remote areas, which results in economic and social disparities across regions. Developing last-mile telecommunication technologies for rural/remote areas is crucial for the computing and ICT services needed to bring billions of rural stakeholders into the digital age. This is particularly true as developed countries turn to “Big Data” and cloud computing to solve the urgent problems of global climate change and emerging contagions. This article focuses on those aspects of providing practical last-mile rural telecommunication access such as interfering factors, technology options, and deployment trends. This article aims to guide service providers, industry practitioners, and local entrepreneurs on the selection, deployment, and operation of suitable telecommunication networks.
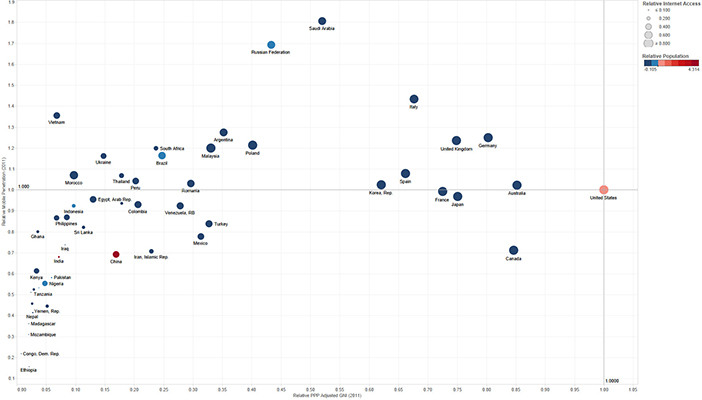 A schematic representation of cellphone vs. Internet penetration of 50 countries with their Gross National Income (GNI).
A schematic representation of cellphone vs. Internet penetration of 50 countries with their Gross National Income (GNI).Mobile technology is also changing economic life in parts of developing world, where individuals are using mobile phones for microfinance, health, and knowledge dissemination. To better understand the impact and potential benefits of mobile phone use in developing countries and emerging markets, we are examining factors that influence adoption of mobile phone technology. Using mobile adoption (MA) as an indicator, we have performed a meta-analysis of global data and identified a set of factors that determine affordability in the context of the global mobile phone phenomenon. Particularly in today’s dynamic world, that economy, as represented by Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), may not be the sole governing factor determining MA. We have identified monthly cost of mobile subscription and average post-paid and prepaid connection charges as significant factors that impact affordability. We therefore have reasons to consider that other technologies and necessities have an equal potential to achieve maximal adoption through a price-adjusted model that accounts for local needs and financial capacity. Given proper infrastructure, price is an entity, which can be adjusted. Adoption of the technology itself will require awareness and appropriate education within the context of local stakeholders. This can provide insights into the adoption of other necessities such as medications, healthcare, household electric devices, water sanitation systems, etc. A manuscript entitled Global Adoption of Mobile phones: Trends and Interfering Factors (Venkatapuram et al.) describing our findings is currently in press and more can be found in our technical report.
Current Project (Pilot Stage): India
We proposed and deployed a network infrastructure to provide education and healthcare services in India where WiMAX base stations provide blanket network coverage in rural areas and outdoor CPEs are used to connect to the WiMAX base station. We observed that video conferencing and related applications can be provided in rural areas for low cost with low bandwidths.